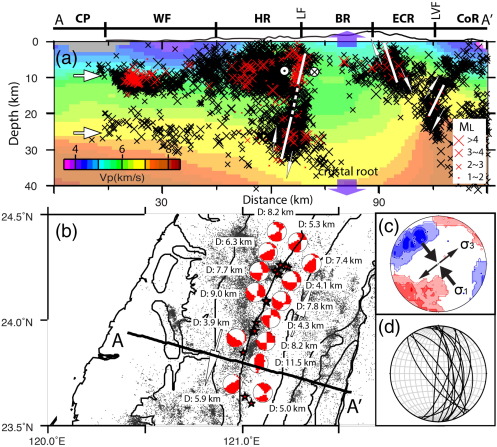
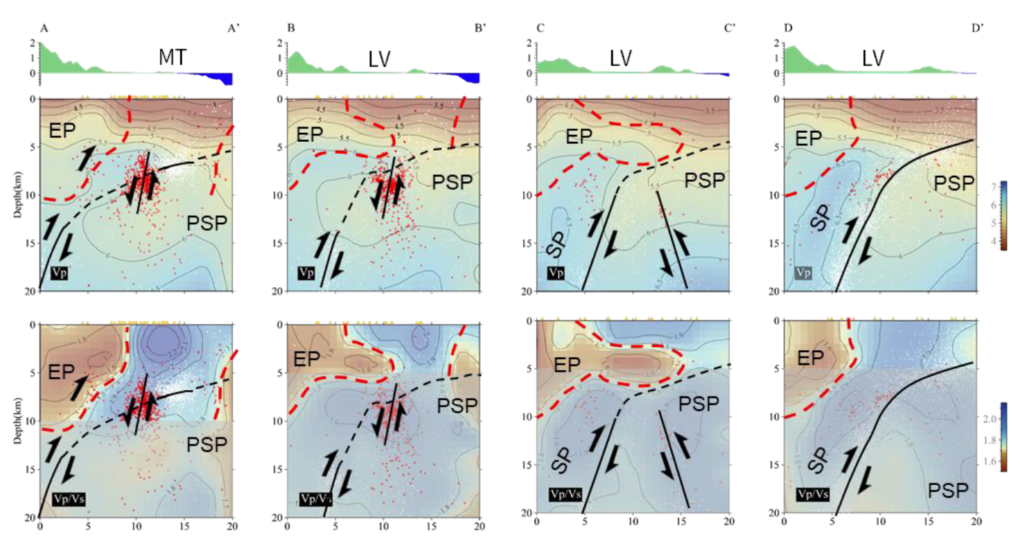
Three-dimensional crustal structure in the northern part of Eastern Taiwan from dense seismic array data sets
- Due to the dense ray coverage of body waves and seismic networks, we further apply both body wave tomography and joint inversion tomography of body and surface waves.
- Combined with the high resolution velocity models and the spacial distribution of these more complete aftershocks, our results clearly depict several local tectonic structures that have not been observed at the northern tip of the Longitudinal Valley, not only a suture but also a transitional area from collision to subduction.
鍾佩瑜 Pei-Yu Jhong
碩士論文:利用密集地震網探討花東縱谷北段地下速度構造
Master’s Thesis: Three-dimensional crustal structure in the northern part of Eastern Taiwan from dense seismic array data sets